(GBAS) GROUND BASED AUGMENTATION SYSTEM (GPS BASED)
FOR AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL (ATC)
REPLACES RADAR SYSTEMS
 |
GBAS, GPS and Air Traffic Control Information and Facts...
|
 |
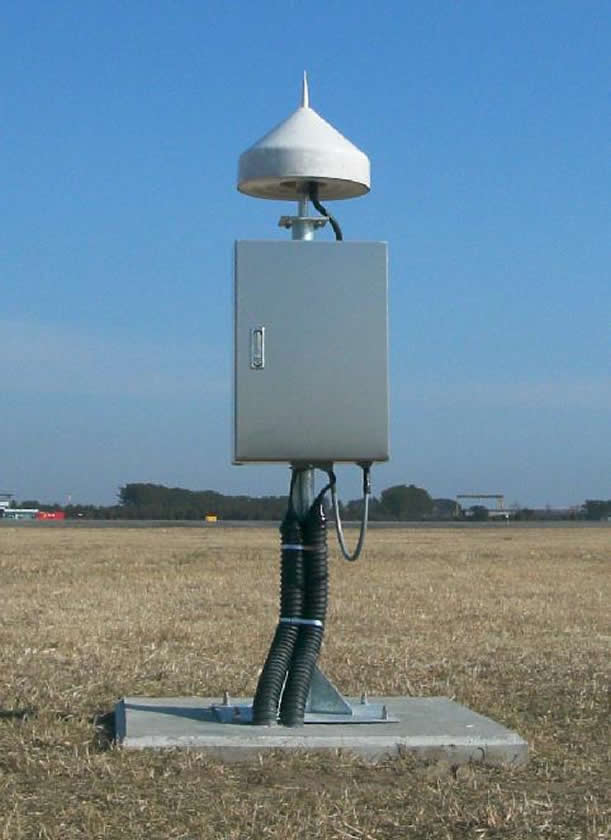 |
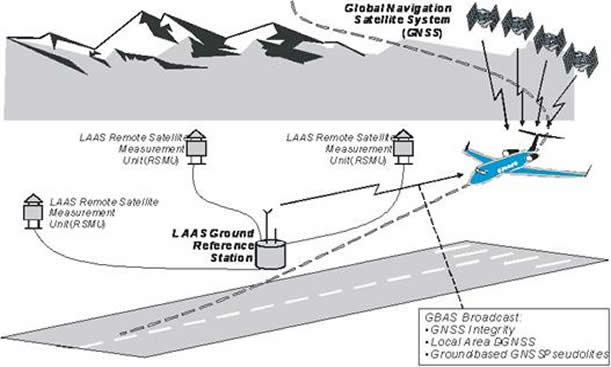
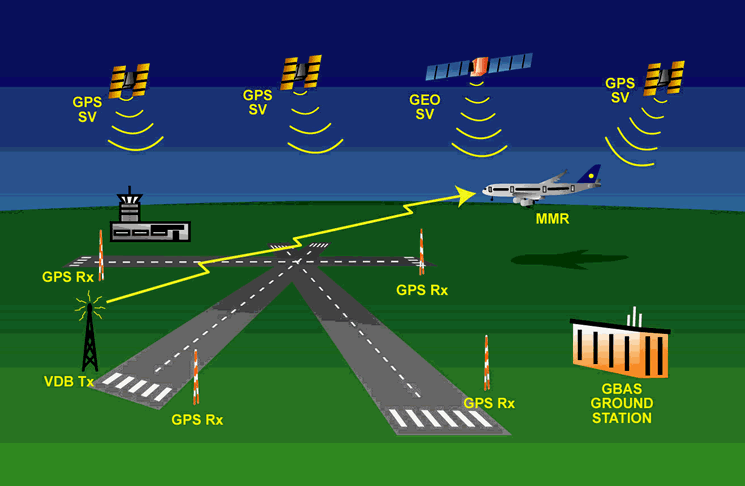
Ground Based Augmentation System (GBAS)Newark Liberty International Airport will pilot a new satellite navigation system designed to reduce flight delays. The New York hub will be the first major airport in the country to test the Ground Based Augmentation System (GBAS). The next generation satellite system is meant to ease air-traffic control congestion and allow planes to fly closer, without reducing safety. The rollout of new technology is part of recommendations laid out by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey's Flight Delay Task Force. Anthony Coscia, Chairman of the Port Authority, said: "As the Flight Delay Task Force concluded, implementing a 'next gen' air traffic control system is critical to reducing flight delays at the nation's airports. "The Port Authority's investment in GBAS shows our willingness to act on the Task Force's recommendation, and we're very pleased that our customers at Newark Liberty will be among the very first to profit from this innovative system." The GBAS project will be partly funded by the Federal Aviation Authority and Continental Airlines. The carrier will equip 15 aircraft with the system and invest in pilot training Background and Overview The Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) is a safety-critical system that augments the GPS Standard Positioning Service (SPS) and provides enhanced levels of service. It supports all phases of approach, landing, departure, and surface operations within its area of coverage. The current Instrument Landing System (ILS) suffers from a number of technical limitations such as, VHF interference, multipath effects (for example due to new building works at and around airports), as well as ILS channel limitations. GBAS is expected to play a key role in maintaining existing all-weather operations capability at CATI/II and III airports. GBAS CAT-I is seen as a necessary step towards the more stringent operations of CAT-II/III precision approach and landing. The operational benefits of GBAS include: |
 |
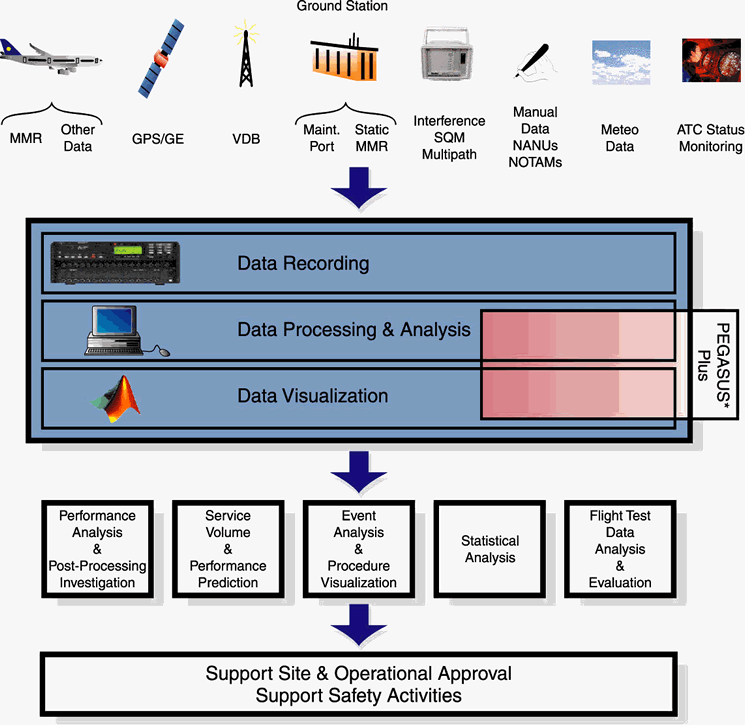
| The Holistic Approach and the GBAS Safety Assessment Process
Until now, aviation has relied almost exclusively on systems developed to its own specifications for positioning and navigation services. This is not to be the case for GNSS, the control of which largely lies outside aviation. Aviation therefore has to use services of third party providers to meet performance requirements and shall have regard to the safety significance of those externally provided services. This leads to a change in the traditional approach to safety management and the organisation thereof. EUROCONTROL has been the mainspring of the development of common safety management policy, procedures, methods and tools and the EATMP GNSS Programme is instrumental in promoting the holistic end-to-end safety assessment approach for space-based navigation services. Following the recent experience related to the development of a Safety Case for the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS), the EUROCONTROL GBAS Project has adopted a pro-active approach to the safety activities that will accompany the overall lifecycle of GBAS. In line with EUROCONTROL Safety Regulatory Requirements (ESARRs) 3 and 4 and in close co-operation with the Safety Regulation Commission (SRC), a risk-based approach is applied to GBAS with regard to the total aviation system. Material developed within the framework of the GBAS Safety Assessment activities provides guidance to the EUROCONTROL/ECAC States / Air Navigation Service Providers and/or Airport Authorities on how to conduct a specific GBAS Safety Assessment at a national/local level to provide evidence that GBAS-based CAT-I operations are tolerably safe. |
 |
© AviationExplorer.com - The Website For Aviation Enthusiasts |



